
As discussed in part 1 of this blog post vLLM is a high-throughput distributed system for serving large language models (LLMs) efficiently. It addresses the challenge of memory management in LLM serving systems by introducing PagedAttention, an innovative attention algorithm inspired by virtual memory techniques in operating systems. This approach allows for near-zero waste in memory usage and improves the throughput of LLM serving by 2-4× compared to existing systems.
The Technical Concepts that vLLM is based on
Challenges in LLM Memory Management
Memory Fragmentation: Traditional LLM serving systems manage the key-value (KV) cache memory in a contiguous fashion, leading to significant internal and external fragmentation.
Dynamic Memory Usage: The KV cache grows and shrinks dynamically, requiring efficient memory management to avoid wasting GPU resources.
Decoding Algorithms: Different algorithms have unique memory-sharing opportunities, requiring flexible memory management.
PagedAttention: A Novel Approach
Flexible Memory Allocation: This allows for dynamic resizing of memory usage, accommodating varying input and output lengths across different requests.
Inspiration from Virtual Memory: PagedAttention draws from paging techniques in operating systems, managing memory in blocks rather than contiguous spaces.
Block-Level Management: Memory is divided into small blocks that can be dynamically allocated and shared across requests, minimizing fragmentation and enabling memory sharing.
Architecture of vLLM
Centralized Scheduler: Coordinates the execution across distributed GPU workers, handling the allocation and scheduling of KV blocks.
KV Cache Manager: Manages the KV cache memory in a paged manner, akin to virtual memory management in operating systems.
Support for Distributed Systems: vLLM can handle models that exceed the memory capacity of a single GPU, using model parallelism strategies.
Other Optimizations
Attention Kernel Optimization: Custom CUDA kernels are developed to handle the unique memory access patterns introduced by PagedAttention, optimizing the GPU execution efficiency.
Decoding Scenario Handling: vLLM efficiently manages complex decoding scenarios such as parallel sampling and beam search, utilizing memory sharing opportunities to further reduce resource usage.
A deep dive into PagedAttention
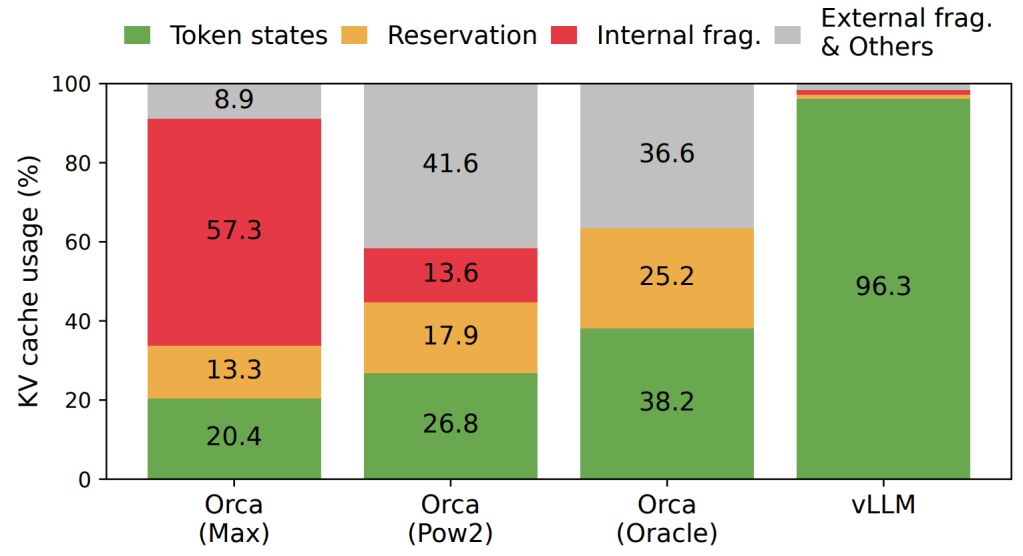
PagedAttention revolutionizes memory management in large language models (LLMs) by addressing the inefficiencies inherent in traditional attention mechanisms. At the core of PagedAttention is the division of the key-value (KV) cache into fixed-size blocks, known as pages. This approach contrasts sharply with the conventional method of storing the entire KV cache contiguously, which often leads to significant memory fragmentation. By partitioning the KV cache, PagedAttention allows each page to hold the keys and values for a fixed number of tokens. This segmentation facilitates more efficient memory usage by enabling non-contiguous storage of these blocks.
The non-contiguous storage capability of PagedAttention is pivotal to its effectiveness. Unlike traditional memory allocation, which requires a continuous block of memory, PagedAttention permits these pages to be stored in separate, non-adjacent locations in memory. This flexibility allows for on-demand memory allocation as new tokens are generated, significantly reducing memory waste. As a result, systems using PagedAttention can dynamically manage memory resources, optimizing the utilization of available GPU memory.
Moreover, PagedAttention excels in enabling efficient memory sharing across multiple sequences. When generating several outputs from a single input prompt, the memory dedicated to the prompt can be shared across different output sequences, thanks to the Copy-on-Write mechanism that PagedAttention employs. This mechanism ensures safe sharing by maintaining reference counts for each block, thereby preventing redundant memory use and enhancing overall efficiency.
The culmination of these features is a marked improvement in throughput for LLM serving systems. By minimizing memory fragmentation and facilitating more efficient batching of sequences, PagedAttention dramatically boosts the throughput, allowing for better GPU resource utilization. This improvement is particularly crucial for handling large-scale models, as it enables faster processing times and supports higher volumes of concurrent requests
Conclusion
vLLM represents a significant advancement in LLM serving systems by addressing the critical challenge of efficient memory management. By leveraging concepts from operating systems, it optimizes memory usage, allowing for increased throughput and reduced latency in serving large-scale language models. This innovative approach not only improves current LLM deployments but also paves the way for future enhancements in AI model serving infrastructure.