The development of multi-agent AI applications, especially those leveraging large language models (LLMs), involves navigating numerous challenges. Ensuring these systems perform optimally requires a blend of strategic planning, robust design principles, and advanced monitoring techniques. Here, we delve into the challenges, best practices, and recommendations for better developing and deploying multi-agent AI applications.
Challenges in Developing Multi-Agent AI Applications
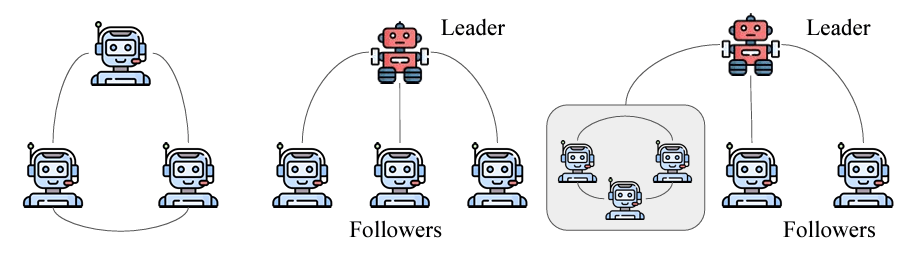
Agent Coordination and Communication:
- Complexity and Scale: Managing interactions among multiple agents requires sophisticated communication protocols and structures. Ensuring that agents can exchange information seamlessly while maintaining performance is crucial.
- Dynamic Behavior: Agents must adapt to dynamic environments and varying inputs, making consistent communication and coordination challenging.
Task Allocation and Role Specialization:
- Specialization: Assigning clear roles and responsibilities to each agent enhances efficiency but requires careful planning to avoid overlaps and ensure all aspects of a task are covered.
Robustness and Fault Tolerance:
- Error Handling: Multi-agent systems must be robust against errors and unexpected interruptions. Implementing fault tolerance mechanisms is essential for maintaining system stability.
Scalability and Performance:
- Resource Management: Efficiently managing computational resources and optimizing the performance of both individual agents and the overall system is critical, especially in large-scale applications.
Security and Privacy:
- Data Protection: Ensuring data privacy and security while enabling effective monitoring and communication among agents is vital.
Integration of Diverse Data Types:
- Multimodal Capabilities: Handling and integrating various data types (text, images, audio) requires advanced multimodal capabilities and efficient data processing techniques.
Ethical and Governance Challenges:
- Bias and Fairness: Addressing biases, ensuring fairness, and maintaining transparency in decision-making processes are crucial for ethical AI deployment.
Human-Agent Interaction:
- User Interfaces: Designing intuitive interfaces for human-agent interaction is essential for usability and effectiveness. The choice between presenting the system as a unified entity or as distinct agents impacts user experience.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities:
- Specialization: Adopt a divide-and-conquer approach by assigning specific roles and responsibilities to each agent based on their expertise. This reduces complexity and improves system efficiency.
- Example: In a customer service application, one agent might handle initial queries, another might manage escalation, and a third could provide detailed analysis and solutions .
Implement Robust Communication Protocols:
- Standardization: Use standardized communication protocols to ensure seamless information exchange between agents. Consider implementing both static and dynamic communication topologies based on the application’s needs.
- Example: In static setups, predefined communication channels simplify debugging, while dynamic topologies enable flexibility and adaptability in real-time scenarios like emergency response systems.
Enhance Fault Tolerance and Recovery Mechanisms:
- Redundancy: Introduce redundancy and autonomous retry mechanisms to handle errors and maintain system stability. Platforms like AgentScope (by Alibaba) provide built-in fault tolerance features that can be customized as needed.
- Example: Use redundant agents that can take over tasks if a primary agent fails, ensuring continuity in critical operations.
Optimize for Scalability and Performance:
- Resource Allocation: Dynamically allocate resources based on workload and performance requirements. Use load balancing and distributed computing frameworks to handle large-scale applications efficiently.
- Example: Implement cloud-based solutions and containerization (e.g., Kubernetes) to scale resources up or down as needed without affecting performance.
Ensure Security and Privacy:
- Encryption and Access Control: Implement robust encryption methods and strict access controls to protect sensitive data. Regularly audit and update security protocols to address emerging threats.
- Example: Use end-to-end encryption for data transmission between agents and apply role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict data access.
Integrate Multimodal Capabilities:
- Advanced Processing: Develop systems capable of processing and integrating text, images, audio, and other data types. This enhances the system’s ability to provide comprehensive insights and responses.
- Example: In a healthcare application, integrate patient records (text), medical images, and audio recordings of consultations to offer holistic diagnostics and recommendations.
Address Ethical and Governance Issues:
- Bias Mitigation: Regularly audit models to detect and mitigate biases. Implement fairness-aware evaluation metrics and transparency frameworks to ensure ethical AI deployment.
- Example: Use diverse and representative datasets for training and regularly update models to correct any biases identified through audits.
Design for Effective Human-Agent Interaction:
- User-Centric Design: Develop intuitive interfaces that facilitate easy interaction between users and agents. Consider whether to present the system as a unified entity or as distinct interacting agents based on user needs.
- Example: In a financial advisory system, provide a single dashboard for users to interact with various agents, each specializing in different aspects of financial planning.
Continuous Evaluation and Improvement:
- Monitoring and Feedback: Implement continuous monitoring and feedback loops to evaluate system performance and user satisfaction. Use dedicated evaluation agents to benchmark and optimize the system regularly.
- Example: Deploy agents that monitor user interactions and system performance, providing real-time feedback to developers for ongoing improvements.
Conclusion
Developing and deploying multi-agent AI applications involves navigating a complex landscape of challenges. By following best practices such as defining clear roles, implementing robust communication protocols, enhancing fault tolerance, optimizing scalability, ensuring security, integrating multimodal capabilities, addressing ethical issues, designing effective human-agent interactions, and continuously evaluating and improving the system, developers can create powerful and reliable multi-agent AI solutions. These practices not only enhance the functionality and reliability of the systems but also ensure that they are ethically sound and user-friendly.
References and Resources
- AgentScope: A Flexible yet Robust Multi-Agent Platform
- Alibaba AI Group Propose AgentScope: A Developer-Centric Multi-Agent Platform with Message Exchange as its Core Communication Mechanism
- The Promise of Multi-Agent AI – Foundation Capital
- Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges
- LLM Multi-Agent Systems: Challenges and Open Problems